Research
Publications | Mississippi Agricultural and Forestry Experiment Station

Assessing the Impact of Ordinances, Outreach and Enforcement on the Resiliency of Gulf Coastal Watersheds
This research tests whether the most ecologically resilient watersheds are those with strong regulations, enforcement, and effective NGO involvement. A GIS database will map relationships between regulations and water quality by compiling codes, ordinances, enforcement actions, and outreach efforts. Year One will develop methods to assess regulatory and NGO effectiveness, supporting broader Gulf initiatives. Results will inform policy recommendations and guide expansion to larger watersheds to define coastal resilience factors.

Beach landscaping to protect the coast
Agricultural engineer Thomas Cathcart and landscape architect Pete Melby developed an experimental beach with limited mechanical maintenance and lots of native plants, which had a dramatic effect on beach erosion in the area. In addition to controlling erosion, this landscaping was designed to keep sand off adjacent highways, reduce the impact of storm damage, and provide other environmental benefits such as filtering pollutants.

Developing Firewise Communities
New community developments can be planned to minimize loss of property and life to wildfire through multiple defensive strategies. A MAFES research project examined three communities affected by the 1998 Florida wildfires and compared them with three recently designed Florida subdivisions that incorporate Firewise principles. Findings show that incorporating multiple defensive strategies in community planning may be effective in wildfire defense.

Development of a Comprehensive Conservation Farm Plan for the MAFES Dairy unit as a Pilot for Future Research
Comprehensive Conservation Farm Planning has been identified as a goal of the U.S. Department of Agriculture and the Natural Resources Conservation Service. The Conservation planning process involves the identification of problems, opportunities and objectives, a resource inventory and analysis, the formulation of design alternatives, and ultimately management decisions. In particular, we aim to develop technology for distribution that would model the effectiveness of agricultural best management practices used in conservation design.

Liquid Gold
Mississippi leads the nation in dependence of ground water-84 percent of our freshwater supply comes from groundwater according to the American Geosciences Institute-and much of that comes from the Mississippi River Alluvial aquifer. Dr. Drew Gholson, assistant professor and coordinator of the National Center for Alluvial Aquifer Research is studying efficient crop irrigation. Dr. Tim Schauwecker, landscape architecture professor, examines how to maintain clean water in agricultural and managed landscape systems by filtering stormwater runoff.
Read More

Model Takes Guess Work Out of Conservation Planning
Conservation planning requires that choices be made among alternative designs and outcomes. Using hydrologic modeling tools in the planning process enables planners to weigh the outcomes of alternative strategies to maximize the effects of implementing conservation practices. MAFES scientists developed a hydrologic calculator in a spreadsheet format that has the potential to put the power of hydrologic decision support into the hands of more landowners.
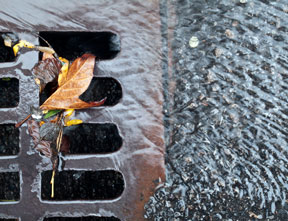
MSU Study Finds Water Quality Overestimated
A MAFES study by professor Timothy Schauwecker found that storm-water management professionals in coastal Mississippi and Alabama often overestimate local water quality. Surveying 70 mostly engineering professionals, 40% rated water quality as "good," despite EPA ratings ranging from "fair" to "poor." The study suggests a disconnect between perception and reality regarding runoff and pollution, emphasizing that education is crucial to improving water quality and storm-water management in these regions.

Parking for Pollinators
At Toyota Mississippi Plant, sustainable communities are being built and improved. Repurposed parking lots were transformed into pollinator gardens using native plants and prescribed fire. Led by prairie expert Dr. Tim Schauwecker, the gardens span nearly six acres and serve as both conservation areas and training grounds. Different treatment zones allow for ecological study and community engagement, supporting Toyota's global commitment to environmental responsibility and sustainable practices.
Read More

Preserving prairie ecosystems
Landscape architect Tim Schauwecker studies methods of conserving prairie ecosystems, which play an important role in creating more sustainable communities. Restoring Mississippi's prairies could boost Mississippi's economy, as well as its ecosystems. In a recent study at MSU, Schauwecker tested seven different plant species native to blackland prairies to determine whether inoculating the plants' root systems with beneficial fungi will help them grow in a prairie environment.

Raising the Roof
The green roof, defined as a building roof covered by vegetation planted over a waterproofed layer, can provide habitat for native flora and fauna. Research has shown that green roofs can also provide relief to city drainage systems and provide extra insulation, which reduces heating and cooling costs. MAFES scientists developed a mix of rooftop species that are cheaper than the usual rooftop plants and that work well in the southern climate.
Read More
